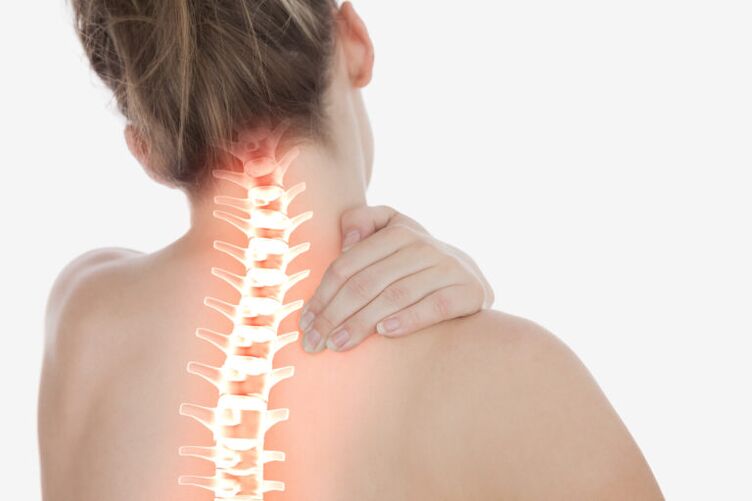
Cervical osteochondrosis or osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a common disease of knowledge workers. Rapidly progressive disease. It is with cervical osteochondrosis, complicated by the development of herniated discs, that an increased incidence of early strokes is associated. For diagnosis, an MRI is required.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
Cervical osteochondrosis is a common cause of neck pain, headache, pressure spikes, shoulder pain, finger numbness, and pain under the scapula. Currently, the frequency of cervical osteochondrosis has increased significantly, as the role of the computer in our life has grown.
However, a fall or injury can stimulate the development of osteochondrosis and degeneration (wear) of the intervertebral discs over time can cause symptoms.
Symptoms
In addition to moderate or mild pain, a feeling of stiff neck, and in some cases reduced mobility, many patients with cervical osteochondrosis experience numbness, tingling, and even weakness in the neck, arm, or shoulder as a result of administration of chemical substances. irritation and pinching of the nerves of the cervical spine.
For example, pinching a nerve root in the C6-C7 segment can cause weakness in the triceps, shoulder or forearm muscles, weakness in the wrist muscles, causing the hand to "hang" and a change in sensation in the the middle finger.
Cervical osteochondrosis often also leads to the development of stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal and other progressive conditions, such as intervertebral hernia. How did this happen?
Osteochondrosis is nothing more than the degeneration of the vertebral structures, caused, as a rule, by the natural aging of the body. With age, thickening of the ligaments, the formation of bony growths on the vertebrae, and other changes occur. When the spinal ligaments thicken or bony growths appear, as well as for other reasons, there is less space for the spinal cord and nerves within the spinal canal. This condition is called stenosis, it is a narrowing of the spinal canal. Severe narrowing of the spinal canal can lead to compression of the nerve roots or even the spinal cord itself.
Intervertebral hernia is also, in most cases, a consequence of degeneration. The intervertebral discs serve as friction absorbers between the vertebrae, thus preventing their destruction. Over time, the disc loses moisture and nutrients, flattens, becomes more brittle and less elastic. As a result, a crack can form in the annulus, through which part of the nucleus pulposus is expelled into the spinal canal. This condition is called an intervertebral hernia. If an intervertebral hernia compresses a nearby nerve root, pain syndrome and / or corresponding neurological symptoms occur.
Diagnosis
Successful diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis begins with a doctor's consultation. The doctor collects the patient's medical history and performs a physical exam to check the mobility and sensitivity of the neck. During the exam, the patient may be asked to perform certain movements and report how pain symptoms change (increase or decrease).
If the exam indicates that more tests are needed, your doctor may recommend radiographic tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT). These diagnostic tests, with varying degrees of reliability, can confirm the presence and location of osteochondrosis, as well as identify other conditions (eg, calcification or arthritis) that may be the cause of the patient's symptoms.
The best option for radiographic examination at this time is MRI, because with the help of an MRI, it is possible to obtain high-quality detailed images not only of bone tissue, as in radiography, but also of the soft tissues of the spine, including muscles, ligaments, vessels, nerves, and intervertebral discs. Computed tomography is usually prescribed if there are any contraindications to MRI, the main of which is the presence of metallic structures or devices in the body (artificial joints, pacemakers, etc. ). The quality of CT scans is lower than the quality of MRIs, but they can also show the condition of the soft tissues of the spine.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis.
Conservative (nonsurgical) treatment of osteochondrosis is always recommended as the main strategy, and surgical intervention is considered only if complex conservative treatment for at least six months has failed or if pain and other symptoms significantly interfere with activities daily patient. .
Methods used in the conservative treatment of cervical osteochondrosis may include:
- spinal traction (traction). The methods of spinal traction without load, which have been used recently, make it possible to completely eliminate the complications of this method of treatment, without which the traction with load cannot work. With an increase in the intervertebral distance, the nutrition of all intervertebral discs improves, the pain syndrome disappears.
- Recovery gymnastics. Recovery gymnastics can improve mobility of the spinal segment. In the mobile vertebral segment, hernias and protrusions do not grow or form, since the intervertebral discs do their job.
- massage therapy.
- drug therapy. It includes NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and pain relievers. In most cases, drug therapy has little or no temporary effect.
- cervical corsets, orthopedic pillows. They may be recommended to stabilize the cervical spine and reduce pressure on the nerve root after trauma and spinal fractures.
Surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis.
If there is no significant relief after six months of conservative treatment and the daily routine becomes difficult for the patient, surgery may be considered. Usually for cervical osteochondrosis, a procedure called spinal fusion is done to immobilize the affected vertebral segment. This surgery involves removing the intervertebral disc, decompressing the nerve root, and placing a bone or metal implant to maintain or create a normal disc space and stabilize the spinal segment.
As a general rule, spinal fusion is performed in one vertebral segment; In rare cases, the question of performing an operation on two vertebral segments may be considered. Be that as it may, the patient should know that surgery to relieve the symptom of neck pain is much less likely to give positive results than a similar surgery to relieve pain in the arm with cervical osteochondrosis. Therefore, if neck pain is the main or only symptom, spinal fusion should only be recommended as a last resort or if all conservative treatments have been tried and failed. If the disc space cannot be identified as the most likely source of neck pain, surgery is best avoided, even if conservative treatment does not provide significant pain relief. Also, do not forget that spinal surgery can have quite serious consequences both in the operated area (local infection, implant rejection, etc. ) and for the whole body (blood clots, allergic reactions to drugs, etc. ). ). Therefore, before making a decision about surgical treatment, it is necessary to discuss all the details of the operation directly with the surgeon who will perform it. It should also be borne in mind that surgery on the cervical spine most often leads the patient to spinal disability.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
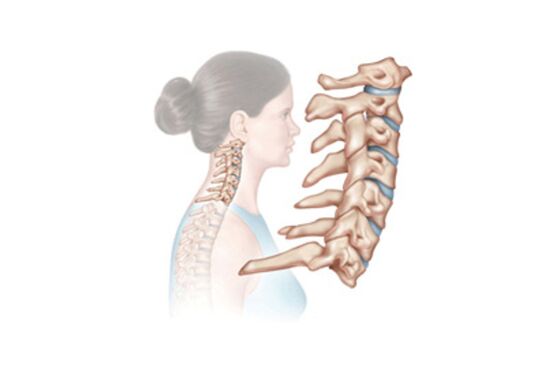
Official medicine interprets osteochondrosis as a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the intervertebral discs.
From which part of the spine these discs are located, the definition of the disease is also given.
Let us specifically consider the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, which accounts for almost 80% of all diseases of our back.
The sad thing is that the disease affects the category of patients between 30 and 50 years old, that is, in the best moment of their work capacity.
In young people, the disease acts as an independent ailment, at an older age it is already a pathology that has developed against the background of other diseases of the joints.
How does the disease develop?
For any part of the spine, a gradual development of the disease is characteristic. Cervical osteochondrosis does not go beyond this framework, so it is worth dwelling in detail on each of its stages.
- In the initial stage, there is a gradual destruction of the intervertebral discs. Between them is located a fibrous ring, in which cracks appear, which causes a decrease in the elasticity and resistance of the discs themselves. They contract and compress the nerve roots.
- The second stage is a consequence of the first untreated stage. The initial destruction of the discs extends to a chronic form, compaction of the tissue occurs, and dislocations of the cervical vertebrae are observed. Head drop syndrome often develops at this stage.
- In the third stage, the pain sensations intensify, constant headaches appear, the sensitivity of the upper extremities is lost, and the cervical "lumbago" is tormented. This is due to the fact that the fibrous ring at this stage is almost completely destroyed.
Often there is a decrease in pain sensations of third-degree cervical osteochondrosis. This happens at the moment when the cartilage tissue disappears and there is nothing to hurt.

Causes
Given the prevalence of osteochondrosis in general, doctors began to closely study its causes. Many of the negative factors have been identified, but there is no definitive list. These are the ones that have been announced to date:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- all kinds of poisonings and infections;
- great physical activity;
- of smoking;
- constant weight lifting;
- stress and nervous tension;
- uncomfortable shoes or an uneven foot that creates unnecessary pressure on the spine;
- improper nutrition;
- frequent hypothermia and exposure to bad weather;
- age-related changes;
- spinal injury;
- bad inheritance;
- a categorical refusal to train, if they have been doing it for a long time before.
Having familiarized yourself with the reasons, it becomes obvious that cervical osteochondrosis can appear at any age. And if at first the symptoms of osteochondrosis are insignificant and marked by rare attacks of pain, then over time it turns out that it is also not possible to turn the neck and it is difficult to tilt the head. And these are not the only dangers of the disease.
What is the danger of the disease
Our neck is a great worker. She is involved all day, and her little vertebrae stoically resist all of our nods and turns. If the bones are displaced, the nerves are pinched and the blood vessels are compressed, and the vertebral artery, which is responsible for nourishing the brain, also passes through the cervical spine. The artery is compressed, the nerve root is compressed, and the inflammatory process begins.

What does this lead to? Spinal stroke, ischemia, intervertebral hernia - these are the serious consequences of cervical osteochondrosis. We add here a general decrease in mobility and osteophyte formation. As a result, we have a disability that threatens total immobility. With such a disappointing prognosis, it is important to quickly recognize the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis.
Symptoms

The shortest way to identify osteochondrosis is the patient's complaints. So what kind of sensations does a person talk about if her cervical vertebrae are destroyed? The picture of the disease looks like this:
- dizziness;
- Strong headache;
- "Flies" and colored spots on the eyes against the background of a headache;
- pain when turning, lifting weights;
- pain that radiates to other organs (heart region, other organs).
Sometimes the signs of osteochondrosis can be classified among other diseases, but they cannot be ignored, even if they are temporary.
Diagnosis and treatment
Continuing with the feelings expressed by the patient, the neurologist proceeds to a more accurate diagnosis of the disease. A few years ago, only X-rays were in the arsenal of doctors to recognize osteochondrosis. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are actively used today. They allow you to accurately determine the stage of the disease.
After evaluating the resulting image, a specialist vertebroneurologist prescribes the necessary treatment. The first thing the doctor takes is pain relief, then swelling and inflammation. To relieve pain, such anti-inflammatory drugs are used. As we recall, the compression of the vertebral artery interrupts the supply of the brain, which means that it must be improved. This is done with the help of muscle relaxants.

Knowing that the symptoms and treatment of cervical osteochondrosis are related to the spine, massage and physiotherapy exercises are necessarily included in the complex of measures to improve health. The massage is performed by a professional and the patient himself. There are also special exercises aimed at developing the cervical vertebrae and restoring their mobility.



















